What Do Lower Bank Deposit Levels Mean for Businesses?
The bank failures in 2023 have taken center stage in financial media coverage, but there is another important banking trend that businesses should be aware of – deposit levels are declining. In fact, FDIC Chairman Martin Gruenberg announced that the first quarter drop was the largest quarterly decline in deposits since the FDIC began tracking the data in 1984.
Bank deposits play an important role in the overall monetary system, but they also have more direct impacts for businesses. Before diving into these implications, it is helpful to understand how deposit levels have changed in recent years.
Recent Trends in Bank Deposit Levels
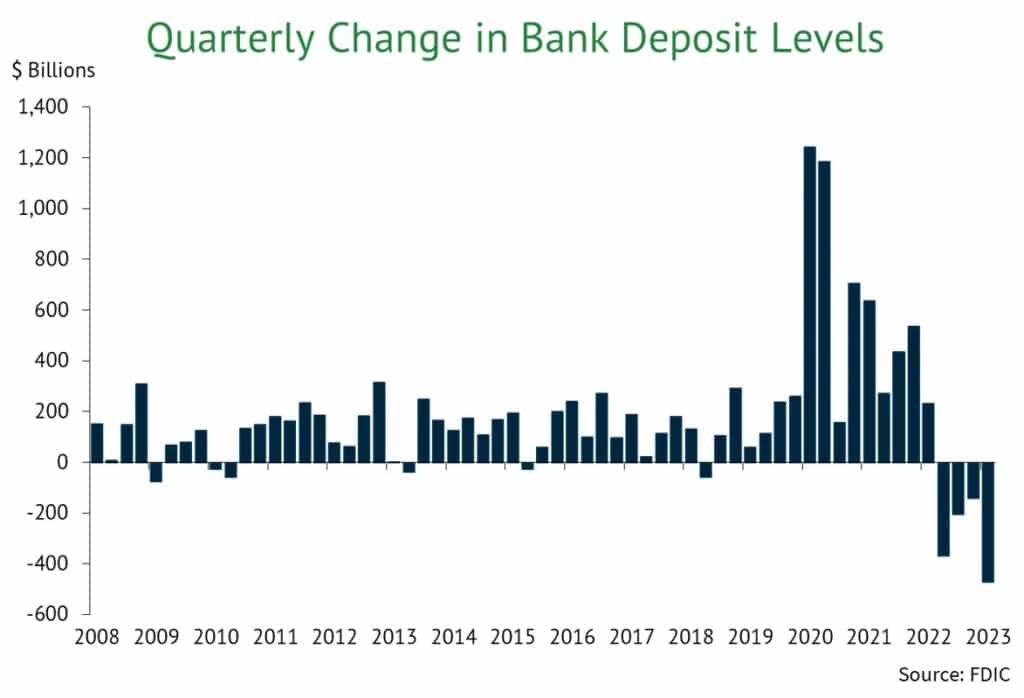
Nationwide, bank deposit levels rose each year from WWII to 2022 and grew particularly quickly during the COVID-19 pandemic. In fact, businesses increased their deposit balances by 34% between March 2020 and the end of 2021. McKinsey estimates that 60% of this growth was due to COVID-19 “surge factors” such as government stimulus and borrowing to increase liquidity.
Heading into 2022, these “surge factors” had begun to lessen, inflation was at a multidecade high, and interest rates were poised to rise. By the second quarter, bank deposit levels were declining. They continued to fall throughout the year and 2022 became the first year in more than seven decades with lower bank deposits. Due to the economic factors at play, this annual decline was not entirely unexpected.
Then, in the first quarter of 2023, turmoil in the banking sector began with the failures of Signature and Silicon Valley Banks. These failures brought the risks of uninsured deposits – those above the $250,000 FDIC insurance limit – to the forefront. During that quarter, uninsured deposits declined by a substantial 8.2%. However, this decline was partly offset by a 2.5% increase in insured deposits.
Including the drop in the first quarter of 2023, bank deposit levels declined for four straight quarters. While official FDIC data has not been updated for the second quarter, Federal Reserve data shows that deposits continued to fall in the second quarter of 2023 as well.
The chart below shows the quarterly change in bank deposit levels from 2008 through the first quarter of 2023. This data clearly shows the abnormal growth during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the substantial decline since that time.
How do bank deposit levels impact businesses?
Businesses often keep significant cash reserves in bank accounts to take advantage of the liquidity and safety they offer as well as the interest income. This interest income is determined by many factors including bank deposit levels.
National deposit levels impact returns mainly due to competition between banks. When the banking system is flush with cash, banks don’t need to lure customers away from their competition with the promise of higher yields. On the other hand, when there are fewer deposits to go around, banks tend to raise their rates above the competition to attract new customers. For this reason, declining deposit levels across the banking industry could lead to greater competition and, indirectly, higher deposit rates.
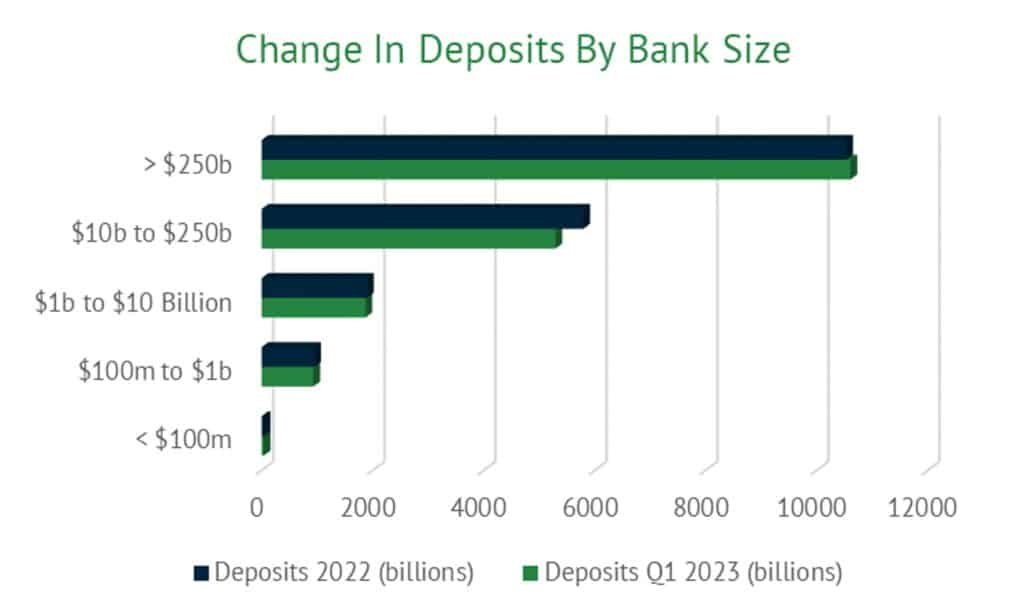
However, national deposit levels only tell part of the story. Bank size, location, and unique position also impact the level of deposits and, therefore, the rates they pay. For example, in the first quarter of 2023, deposits at banks with assets above $250 billion increased by 0.7%, while deposits at banks with between $10 and $250 billion declined by 8.7%.
The chart below shows the change in deposit levels by bank size between 2022 and the first quarter of 2023. As illustrated, smaller banks lost deposits while the largest banks increased their holdings.
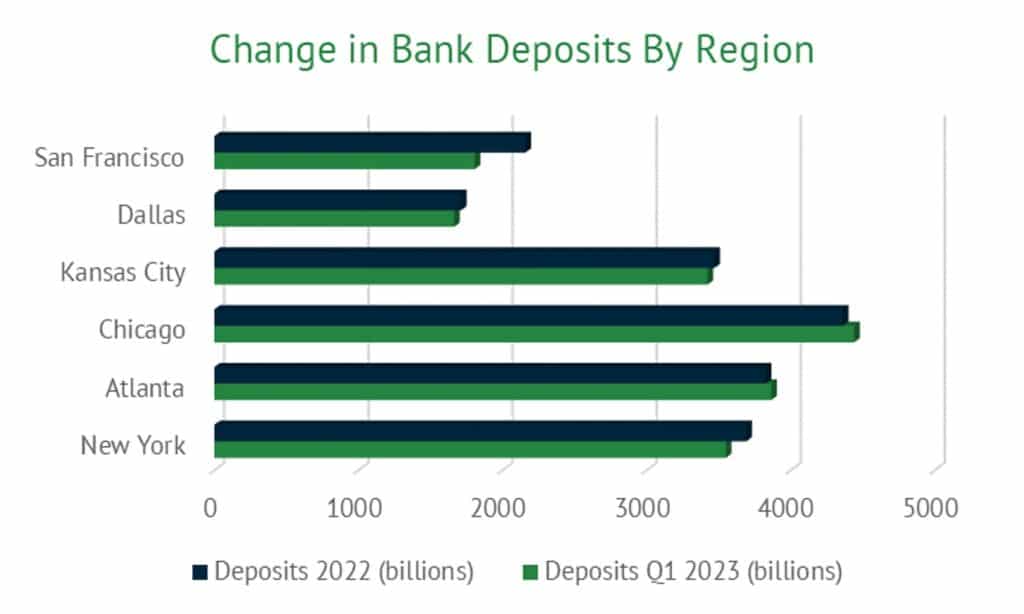
Further, the location of a bank also impacts the trends in deposit levels. As the chart below shows, deposit levels vary dramatically based on region and so do the changes in total deposits. For example, deposits in the Chicago area grew by 1.8% between 2022 and the first quarter of 2023 while banks in the San Francisco area lost 16.3% of deposits.
Because deposit levels and individual bank needs vary so widely, there are opportunities for businesses to earn higher yields in more competitive sections of the market. To capture these yields, businesses could manually monitor rates from banks across the country. However, this process is time consuming. Fortunately, there is an easier way. With advances in financial technology – a.k.a. fintech – businesses can partner with an experienced deposit management firm to access nationally competitive returns along with a host of other benefits.
Nationally Competitive Returns for Business Cash with Marketplace Banking™ By ADM
At the American Deposit Management Co. [ADM], we have developed proprietary fintech which allows businesses to capture competitive interest rates from across the country – without the hassle. We call this concept Marketplace Banking™ and it works through our nationwide network of banks and credit unions that compete for deposits.
In addition to nationally competitive returns, Marketplace Banking™ allows businesses to access extended FDIC / NCUA coverage so that all their cash can be covered by government protection. We accomplish all of this with one account and one monthly statement.
To learn more and get started, contact a member of our team today.
Q4 Banking Trends: Strong Net Income, Rising Deposits, Lower Unrealized Losses
American banks reported strong net income and lower unrealized losses alongside higher loan balances and deposit levels in Q4 2025.
How Did the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act Facilitate Bank Consolidation?
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act passed in 1999 and ushered in a new era of consolidated, one-stop shop banking that perseveres today.
An Overview of Regulations Governing the Management of Public Funds
Public entities like school districts and municipalities are held to specific regulations that govern the ways funds are invested.